1. What is Google Ads?
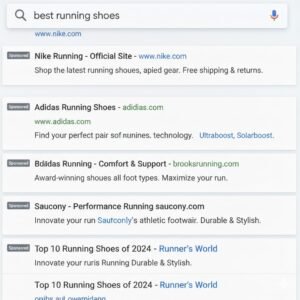
Google Ads is Google’s advertising platform that lets you promote your business across Google Search, YouTube, and other partner sites. It works on a pay-per-click (PPC) model, meaning you only pay when someone clicks your ad.
When a user searches for something like “best shoes for running,” Google shows ads that match that search intent.
Example:
If you sell handmade candles, your ad can appear when someone searches “scented candles near me.”
2. Why Businesses Use Google Ads
Google Ads is one of the fastest and most targeted ways to reach potential customers.
Benefits:
-
Reach billions of active users daily.
-
Choose your target by location, device, interests, and more.
-
Track every click, conversion, and view.
-
Stay in control with a custom daily budget.
Example:
If you offer an online course, you can target users searching “learn Google Ads” and only pay when they click.

3. How Google Ads Works
Every time someone searches on Google, an ad auction happens behind the scenes.
Here’s how it works:
-
Advertisers choose keywords they want to target.
-
They set a maximum bid (how much they’ll pay per click).
-
Google checks each ad’s Quality Score (relevance + landing page + CTR).
-
The best combination of bid and quality appears first.
Example:
If three people bid for “digital marketing course,” Google shows the ad with the best score and bid balance.

4. Types of Google Ads Campaigns
Different campaign types help you reach different audiences:
-
Search Ads: Text ads on Google Search.
-
Display Ads: Visual ads across websites and apps.
-
Video Ads: Ads that play on YouTube videos.
-
Shopping Ads: Product ads with images and prices.
-
App Ads: Promote mobile apps across Google networks.
-
Performance Max: Combines all formats using automation.
 5. How to Create a Google Ads Campaign (Step-by-Step)
5. How to Create a Google Ads Campaign (Step-by-Step)Follow these steps to set up your first campaign:
-
Go to ads.google.com and log in.
-
Click “New Campaign.”
-
Choose your goal (sales, leads, or traffic).
-
Select your campaign type (Search, Display, etc.).
-
Set your daily budget and bidding strategy.
-
Define your target audience and location.
-
Add keywords relevant to your business.
-
Write engaging ad headlines and descriptions.
-
Review your settings and publish.
Example:
Ad Headline: “Learn Digital Marketing – Join Free Class Now!”
Ad Description: “Master Google Ads with our certified online course. Enroll today!”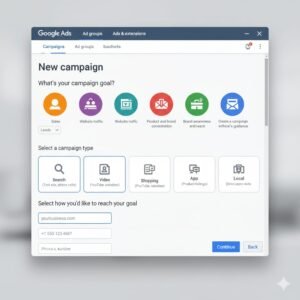
6. Understanding Keywords and Bidding
Keywords are the base of every Google Ads campaign.
Types of Keyword Matches:
-
Broad Match: shows for similar searches.
-
Phrase Match: shows when the phrase appears in the search.
-
Exact Match: only shows for that exact keyword.
Example:
Keyword “Digital Marketing Course”-
Broad: “Best course for online marketing”
-
Phrase: “Learn digital marketing course”
-
Exact: “Digital Marketing Course”

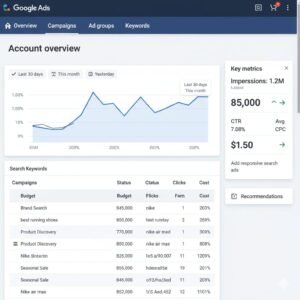
7. Tracking and Optimization
Once your ad is live, track its performance using:
-
CTR (Click-Through Rate): % of users who click your ad.
-
CPC (Cost per Click): What you pay per click.
-
Conversions: Number of users taking action (buying, signing up, etc.).
-
ROAS (Return on Ad Spend): How much you earn per ad dollar.
Use tools like Google Analytics and Conversion Tracking to measure success and adjust campaigns.
8. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoid these beginner errors:
-
Targeting too broad an audience.
-
Skipping negative keywords.
-
Ignoring conversion tracking.
-
Using weak headlines or unclear CTAs.
-
Forgetting to test multiple ad versions.
9. Pro Tips for Better Results
-
Use catchy headlines and clear CTAs.
-
A/B test your ads regularly.
-
Add ad extensions (sitelinks, callouts, location).
-
Optimize your landing page for mobile users.
-
Track your results weekly and adjust bids or keywords.

10. Conclusion
Google Ads isn’t just about spending money — it’s about strategy, testing, and improving. Once you understand how keywords, targeting, and ad quality work together, you’ll start seeing real results.
Keep testing, stay consistent, and use your data to guide your next move.
-
